Puddle Lab
Started 22nd January 2022
A machine that watches puddles evaporate
I tried various techniques for monitoring the water level in the crawl space under my house (see Sensor) but was not happy with the results, I wondered what would be a method that gave the best results regardless of cost. I am expecting to measure the water level accurate to less than 1 millimetre over a range of 50 millimetres. The water is dirty, but there is an open expanse of it. The sensor has to be battery powered and reports its measurements by radio.
The method I thought of is to lower a capacitive proximity probe (LJC18A3-H-Z/BX) towards the water, this will trigger before it encounters the water. There are parallels with Z probing a 3D printer bed. This is an "expensive" approach because it involves mechanics which will wear and use more energy.
The first version used a B-04E (see XYP) stepper motor and screw mechanism taken from DVD or CD drives. This has a range of around 50 millimetres but at the time I attempted to set up the sensor the water was almost too deep for it. I made a second version using a 3D printed linear actuator which has a bigger range.
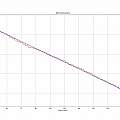
First version using DVD drive stepper motor.
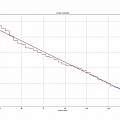
Second version using 3D printed linear actuator.
The sensor also measures temperature and humidity and to test it I set it above a small saucer of water for several days and checked if it could measure the evaporation.
The graphs show the depth against time for both versions, it is apparent resolution is between 0.1 and 0.2 mm - because the depth moves in steps of that size. The resolution is plausibly explained by the size of the motor steps. Over in 3D printer land (see Zprobe) the capacitive proximity probe is found to have an accuracy around 0.01 mm.
The sensor reads the depth every half-hour, typically there are half a dozen repeated values before the next step down. Red curves are the data and blue a linear least squares fit. The gradient of the fit is around 0.014 mm per hour.
Could I look up how fast water evaporates to check this value, not so simple. Yes results depend on humidity and temperature and are proportional to area and time, but often there are other things to worry about, like wind, waves and sunshine, none of which were present in my workspace.
It is apparent that after a long spell with no rain the water dries up. Also if there is sufficient water to flood the ground outside (it has happened) every mm of rain will result in a mm increase in depth of water in the crawl space. But what is the relationship between water level and rainfall in between.
Deploying Puddle Lab to the crawl space...
I imagined that the water depth under the house would be related to the general water table level in the area and would increase and decrease slowly. It turns out the model which fits the results best is an inverted cone shaped tank connected to the downspout from the roof. When the underfloor space has been dry the depth increases rapidly at a rate many times the rainfall. As the depth increases the rate becomes closer to the amount of rainfall. Eventually the rate is less than that of rainfall - presumably surface drainage starts to remove water.
When it is not raining the depth decreases at around the evaporation rate (no sign of the water running back out) - the crawl space is fairly warm and ventilated.
The first graph shows the depth of crawl space water (red) compared with the amount of rainfall (blue). I've made the rainfall level agree with the depth at the start. January 2022 was dry and this is the position the data starts from, rainfall early in February caused a rapid increase in depth - alas before I started to gather rainfall data.
Video of motion:
Electronics
The electronics are similar to my previous efforts see Sensor. I used an Arduino Pro Mini with the power LED disabled. I found the on-board regulator quiescent current was around 1μA which was good enough. To get the DVD mechanism to shift the capacitive probe I had to power it from 12 V. I also doubted the viability of the probe and the A4988 motor driver at 5 V.
To get the 12V I used two 6 V 5 AH lead acid batteries. The idea was that a probe event would use 1 A for around 10 seconds. 5 AH is 5*60*60 As and at 48 probes per day around 37 days power.
There is some messing about turning the power to various components on and off, a power MOSFET is involved.
Arduino source code:
3D print files
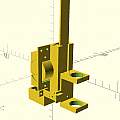
The B-04E DVD stepper/screw has a hole in the metal frame which it happens fits a TCRT5000 reflective optical sensor, in addition the "nut" which is driven along the screw is white nylon and makes a good target for the TCRT5000. The 3D model for holding the B-04E mechanism is an improved version of the one in XYP supporting the TCRT5000 and stopping the nut from partially rotating. The TCRT5000 allows homing the mechanism - drive the nut upwards until the sensor triggers.
The B-04E motor takes 20 full steps to perform one rotation - each step 20 degrees. The screw advances the nut 3 mm per rotation. I set up the A4988 motor driver to have 8 microsteps per full step. As a result distance in mm equals (0.15/8)*microsteps.
The method of measuring liquid depth is to assume the mechanism sets off from around the homed (maximum height) position and drive it downwards until the capacitive probe triggers (noting the position). Then drive the mechanism upwards until the TCRT5000 triggers (again noting the position) indicating the mechanism is homed. The depth is then the difference between the two trigger positions.
Linear Actuator version
This uses a 28BYJ-48 stepper motor, popular for Arduino projects. I picked the 12V version and I modified it to have four wires and work with the A4988 driver. The mechanism is a rack and pinion, an ITR9606 opto-interrupter is used to detect the home position. The idea is the same as the B-04E version, but the homed signal state is opposite - other than that the code is the same.
There are 32 steps per revolution and a gearbox with ratio 63.68395, the rack has 3.25 mm per tooth and the pinion 14 teeth. I set up the driver for 2 microsteps per step. As a result distance in mm equals = 1/2*1/32 * 1/63.68395 * 14 * 3.25 microsteps, or 0.0112 microsteps.
I took inspiration from Thingiverse, in particular the code relies on 28BYJ-48 model from RGriffoGoes www.thingiverse.com/thing:204734 and OpenScad Rack & Pinion generator from racatack https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:1645390
David Pilling's Wiki
Set view